Introduction to Deep Tissue Massage and Athletic Recovery
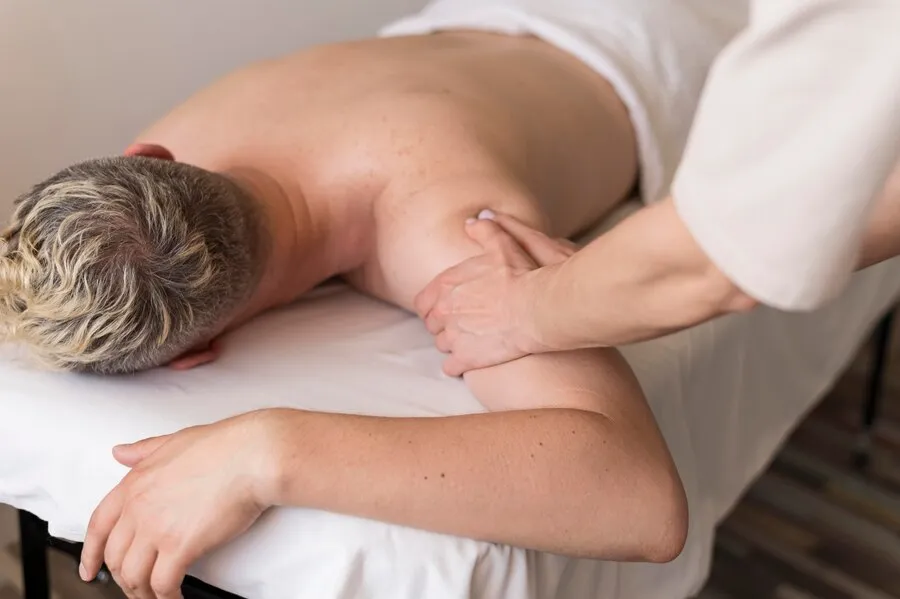
Deep tissue massage is a crucial recovery method in sports. It focuses on the myofascial layers to promote healing and alleviate micro-traumas. It helps alleviate delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS), which can result from lactic acid accumulation from intense physical activity, thus accelerating the body’s recovery process.
For endurance athletes and weekend warriors alike, pursuing peak performance inevitably introduces stress and strain to muscular fibers. It is where the magic of Deep tissue massage makes an impressive entrance. Its application transcends soothing sore muscles, and more importantly, it contributes to an athlete’s longevity in sports and regular training. Enhancing blood circulation and facilitating scar tissue breakdown sets the stage for robust post-exercise muscle recovery.
The Science Behind Deep Tissue Massage
Deep tissue massage is beneficial for athletes as it helps release adhered tissues, eliminate toxins, and promote nutrient supply for muscle recovery. Massage stimulates blood flow, promoting oxygenation and nutrient supply. It also relieves tightness and chronic muscle tension by breaking knots and releasing endorphins, the body’s painkillers. Regular massage also leads to psychological benefits such as decreased anxiety and heightened well-being, essential in competitive settings. The benefits extend beyond physiological benefits, as athletes report decreased anxiety and heightened well-being.
Deep Tissue Massage Techniques
Sports-specific muscle areas that are tight and immobile can be treated with deep tissue massage. Therapists use techniques like stripping, friction, and trigger point therapy to reach deep-seated tension patterns. Stripping involves applying pressure along muscle fibers to break down knots, while friction realigns tissue fibers and promotes healing. Trigger point therapy targets hyperirritable spots in muscles with repeated cycles of isolated pressure and release. Athletes must communicate with their massage therapists about the stroke intensity and sensations, and the masseur’s manipulation should be guided by their tolerance and specific areas of concern to ensure a beneficial and comfortable experience.
The Role of Deep Tissue Massage in Reducing Injury Risk
Overuse injuries can significantly impact an athlete’s performance and prospects. Proactive approaches like deep tissue massage are crucial for maintaining muscle tissue and fascia’s elasticity and flexibility, addressing existing aches, and protecting against repetitive motion injuries. Regular sports massage and intense tissue therapy can prevent prolonged injuries and improve recovery periods, allowing athletes to return to training and competitions with improved tissue function and range of movement.
Integrating Deep Tissue Massage into an Athletic Training Regime
Deep tissue massage is crucial to an athlete’s routine, ideally planned with strenuous training cycles or after competitive events. It can provide an edge, allowing athletes to work harder and recover faster. Massage therapy is an integral part of a regular training framework, similar to a well-tuned diet and customized workout plan. It should be routine, purposeful, and aligned with individual goals and schedules.
Read Also: Wellness Redefined: Exploring the Integrative Approach to a Healthy You
Alternative Massage Therapies and Their Comparison to Deep Tissue
Deep tissue massage is a popular therapy among athletes but is not the only option. Alternatives include Swedish massage, sports massage, and trigger point therapy, each with benefits. Swedish massage promotes relaxation and circulation, while sports massage targets overused and stressed areas. Deep tissue may not always be the most suitable choice for athletic recovery, so understanding the different techniques and their specific benefits is crucial for making the best decision for an athlete’s unique situation.