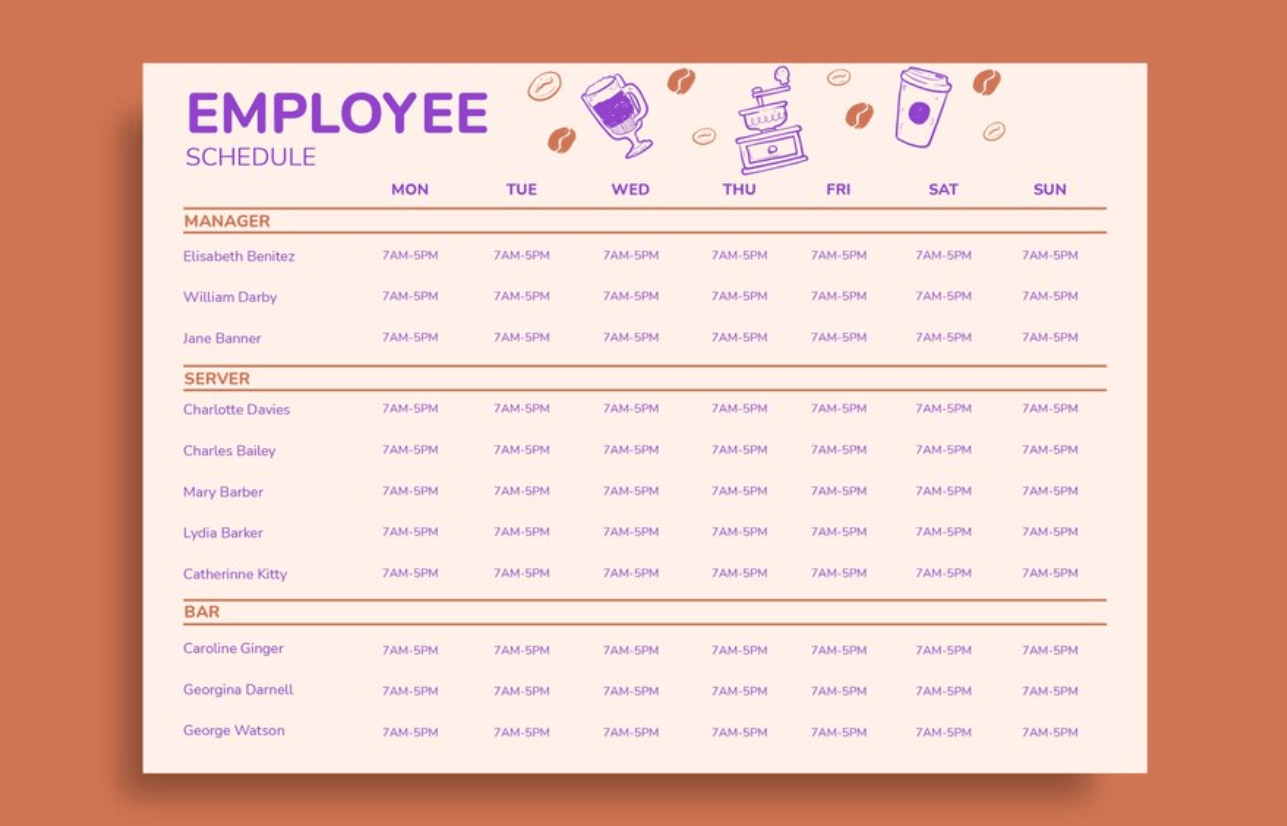
Table of Contents
Organizing employee work schedules goes beyond simply assigning hours. It’s a carefully crafted process that balances the business’s operational requirements while addressing employees’ individual needs and preferences. A well-structured schedule can directly impact productivity and employee satisfaction, making it essential for any manager to understand the details of scheduling.
Types of Employee Work Schedules
A key aspect of managing schedules is knowing the different types and when to deploy each to meet business demands effectively. Full-time work schedules typically involve 40 hours per week, often spread across a predictable and consistent 9-to-5 framework. These schedules are common in industries that require stability and long-term commitments. Salaried employees generally fall into this category, and their schedules do not fluctuate drastically week by week.
In contrast, part-time work schedules are far more variable. They offer flexibility, usually demanding fewer hours from the employee each week, and often operate on an hourly wage system. Ideal for businesses like retail or food service, part-time schedules allow companies to maximize labor availability during peak periods without the overheads associated with full-time employees.
For businesses that need to accommodate employee preferences or provide more control over their hours, flexible work schedules offer a suitable alternative. These arrangements allow workers to align their hours with personal obligations, improving morale and retaining talent that may otherwise be lost to rigid scheduling policies. However, with increased flexibility comes the challenge of ensuring that core organizational needs are met.
Some businesses require more complex scheduling mechanisms, such as split shift schedules, where employees work two separate periods in a single day, often with a long break in between. This format is especially useful in industries like hospitality, where demand spikes during specific hours. Similarly, rotating shift schedules, which cycle employees through day, night, and weekend shifts, are often found in industries with 24/7 operational needs, like manufacturing or healthcare. Examples of such rotating schedules are the DuPont schedule, which cycles employees through day and night shifts with a full week off each month, and the Pitman schedule, a two-week cycle that offers breaks between night and day shifts to prevent worker fatigue.
Yet another form of scheduling that offers employees a balanced workload is the compressed work schedule. This type allows employees to work longer on fewer days, such as four 10-hour days instead of the standard five 8-hour days. Though it may reduce the frequency of an employee’s workdays, it requires careful planning by managers to ensure there’s adequate coverage throughout the week.
Finally, industries such as healthcare and emergency services might utilize on-call work schedules. In these scenarios, employees are expected to be available at short notice, ready to fill shifts when emergencies or unpredictable service needs arise.
Creating an Effective Employee Work Schedule
The creation of a work schedule is not a simple one-size-fits-all endeavor. The process begins with an assessment of staffing needs. This involves understanding the demands for each upcoming shift, including estimating peak hours of operation. These estimations are particularly important in industries such as retail, where customer foot traffic can vary throughout the week. Managers must allocate employees to shifts based on the quantity of available workers and the skillsets required to meet customer or operational needs.
Once the staffing requirements are known, it’s essential to forecast demand for each shift, using historical data and predictions based on expected peak times. Analyzing previous scheduling data can reveal patterns, helping managers anticipate when more staff coverage will be necessary due to high customer demand or increased workloads.
It’s equally important to factor in employee preferences, as allowing employees to voice their shift preferences can help boost morale and ensure better coverage for harder-to-fill shifts. Managers can gather this data by discussing preferences with employees directly or through surveys where workers indicate their availability. Engaging employees in this manner increases overall job satisfaction, reduces absenteeism, and improves workforce stability.
Preparation is also required in case of absences or last-minute changes. Managers should create shift replacement plans to handle sick leaves or emergencies. Backup systems, such as maintaining a list of staff available for extra shifts, can mitigate disruptions to normal operations without causing undue stress.
Lastly, to maintain compliance with labor laws, particularly those related to work hours and rest periods, schedules must be vetted for legal and internal policy requirements. For accuracy, many businesses rely on automated scheduling tools that simplify these processes while ensuring compliance with laws, such as dictating breaks between shifts or prescribing limits on consecutive work hours.
Integrating Tools for Efficient Scheduling
Integrating various tools and software applications plays a pivotal role in creating seamless work schedules. For managers looking to streamline their scheduling process, leveraging technology can greatly reduce the time spent on planning and adjustments. One practical tool is the use of an online calendar system. These systems allow managers and employees to sync schedules, check availability, and easily organize shifts without discrepancies. By offering real-time updates and notifications, these calendars ensure that all parties can access up-to-date schedules. Additionally, incorporating a schedule maker, an automated tool designed specifically for creating and managing work schedules, can minimize the likelihood of errors and help match employee skills with the required shifts effortlessly.
Moreover, platforms facilitating communication and feedback can enhance the scheduling process. For instance, implementing a messaging board within the scheduling software can help address concerns and conflicts swiftly. This can empower employees to proactively swap shifts or adjust their availability, leading to greater autonomy and satisfaction. Equally, managers can efficiently oversee schedules and maintain compliance with workplace regulations by having a centralized view of employee shifts and preferences. Hence, integrating diverse tools such as cloud-based storage for accessing documents and time-tracking applications not only optimizes operational efficiency but also fosters a collaborative environment for crafting effective work schedules.
Best Practices in Scheduling
Once employee preferences, legal considerations, and managerial requirements are fully understood, the focus must shift to creating transparent, simple, and predictable schedules. A key factor in this is ensuring the schedules are published well. Giving employees the information they need to plan their own time creates a healthier work-life balance and avoids conflicts that arise from last-minute scheduling.
Encouraging regular feedback throughout the scheduling process can further refine it. Employees who feel empowered to provide insights are also more likely to feel satisfied with the structure of their shifts and contribute to operational efficiency. Scheduling platforms with built-in communication tools allow employees to submit requests for shift changes or time off without delay, reducing miscommunication between management and staff.
Another important aspect of effective work scheduling is creating clear protocols for shift changes. By establishing a well-documented system for handling changes—whether requested by an employee or necessitated by unforeseen circumstances—managers can minimize misunderstandings and ensure continuous coverage without undue strain on the team.
Finally, simplicity in design is key. Schedules ought to be easy to read and understand at a glance. Complicated or unclear schedules increase the chances of missed shifts or scheduling conflicts, leading to operational inefficiencies. A clear, comprehensible design reduces inquiries, administrative overhead, and improper staffing during important times.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Even the most well-thought-out schedules present challenges, particularly when accommodating part-time and full-time employees. Balancing these two groups while ensuring consistent shift coverage is essential for maintaining efficient operations. Managers can overcome this by standardizing processes for offering variable shifts to part-time employees without reducing flexibility for full-time staff.
Another challenge arises from last-minute changes. Handling unanticipated shifts, unexpected time-off requests, or other scheduling conflicts can be simplified by having a pre-agreed-upon replacement system, allowing the business to function despite short-term complications. Furthermore, using automated scheduling systems that flag potential conflicts, such as overlapping shifts or excessive overtime, helps reduce avoidable errors.