Key Takeaways
- Understanding emerging trends in network security is crucial for staying ahead of cyber threats.
- Adopting new technologies can improve network security infrastructure and protection measures.
- Increased collaboration among organizations and experts can enhance overall cybersecurity effectiveness.
Introduction to Network Security

Network security is an ever-evolving landscape, with new threats and technologies continuously reshaping the field. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, companies need to prioritize network security to protect their data and digital assets. As we move further into the digital age, understanding these changes is more important than ever. This article delves into the future of network security, highlighting key trends and predictions to keep an eye on.
The complexity of modern cyber threats necessitates a proactive approach. Investing in robust security measures and staying informed about the latest developments in the field can make all the difference. Whether it’s a multinational corporation or a small business, understanding the landscape of network security helps organizations stay resilient against potential threats.
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
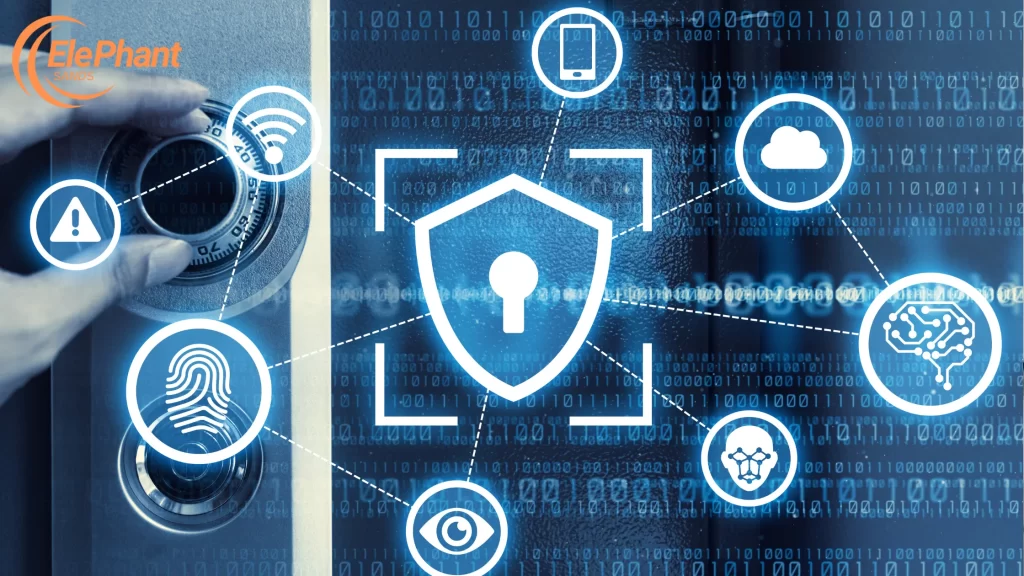

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to revolutionize network security. These technologies, designed to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and detect anomalies, can significantly improve security measures. Integrating AI and ML will enhance the ability to predict and mitigate cyber-attacks and streamline the incident response processes.
Advantages of AI and ML
- Faster threat detection and response times: AI and ML can rapidly process data. This means that potential threats can be identified and addressed much faster than traditional methods, reducing the margin for damage.
- Reduced need for manual monitoring: Automation systems allow for continuous tracking without human intervention, freeing up IT resources for more strategic tasks and reducing the risk of human error.
- Improved accuracy in identifying real threats versus false positives: AI’s capability to learn from each incident ensures that the system only identifies genuine threats over time, thereby increasing accuracy and reducing false alarms.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust is fast becoming a fundamental principle in network security. This approach ensures that no user, inside or outside the network, is trusted by default. Every attempt to access network resources is verified to enhance security and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Implementing Zero Trust
- Verify every user, device, and connection: Zero Trust requires verification of each entity trying to access the network, no matter where the request originates from, to ensure authenticity and security.
- Implement robust authentication methods: Employ multi-factor authentication (MFA), biometrics, and other advanced techniques to ensure that users are who they claim to be.
- Continuously monitor and log network activity: Real-time monitoring and logging are essential to identify and respond to suspicious activity promptly.
Cloud Security Enhancements
With the increasing reliance on cloud services, securing these environments is paramount. Enhanced cloud security measures, including advanced encryption methods, are being developed to protect data stored and processed in the cloud. Organizations must stay updated with these innovations to safeguard their cloud assets. Cloud providers are also rolling out advanced security tools to help companies meet compliance requirements and protect sensitive data against breaches.
IoT Security Challenges
As the Internet of Things (IoT) grows, so do the associated security challenges. Millions of connected devices create a vast attack surface for cybercriminals. Implementing robust IoT security protocols is essential to protect these devices and their networks. As devices become more innovative and integrated into daily operations, securing them cannot be overstated. Attack vectors like malware and DDoS attacks are notorious in the IoT realm.
Securing IoT Devices
- Use strong, unique passwords for each device. For IoT devices, Avoid using factory settings or simple, easy-to-guess passwords. Change default passwords immediately upon deployment.
- Ensure devices are regularly updated: Firmware and software updates often include crucial security patches. Regularly updating devices is critical to mitigating vulnerabilities.
- Segment IoT devices onto a separate network: Keeping IoT devices on a different network than a business’s essential operations can limit potential damage in case of a breach.
Collaboration and Information Sharing
Collaboration is critical in the fight against cyber threats. Organizations and cybersecurity experts must collaborate, sharing information and best practices to stay ahead of potential attacks. Initiatives like these can significantly enhance the industry’s overall security posture. Collaborative platforms and threat intelligence sharing act as force multipliers, helping identify and neutralize threats faster.
Human Factors in Network Security
Despite technological advances, the human factor remains a critical element in network security. Training and awareness initiatives are crucial in ensuring that employees grasp the significance of cybersecurity and follow proper protocols to avoid breaches. Education and constant training are essential because human error is a major vulnerability. Regularly updating employees about new threats and conducting drills can reduce the risk of successful attacks.
Key Areas of Focus
- Regular phishing awareness training: Educate staff on how to identify phishing attacks and prevent being tricked by these fraudulent schemes.
- Encouraging strong password policies: Enforce solid and unique passwords and provide tools like password managers to help employees manage them.
- Promoting a culture of security within the organization: Ensure that security is seen as a crucial aspect of the company culture, making sure every employee comprehends their responsibility in safeguarding organizational data.
Regulatory and Compliance Landscape
Regulations and compliance requirements are becoming more stringent, shaping how organizations manage network security. Keeping up with these changes is essential to avoid penalties and ensure robust security measures are in place. Complying with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA avoids legal repercussions and builds Trust with customers and stakeholders. Staying abreast of regulatory changes helps organizations adapt their security strategies proactively.
To understand the regulatory landscape, check out this list of top cybersecurity regulations and compliance requirements compiled by industry experts.
Read More: Evaluating CCaaS Providers: Key Factors to Consider
Final Thought
The future of network security is both exciting and challenging. By staying informed about emerging trends and adopting new technologies, organizations can better protect themselves against ever-evolving threats. From AI and ML advancements to zero-trust architectures, the security landscape will continue to evolve, requiring vigilance and adaptability. It’s a continuous battle, but we can stay one step ahead of cyber threats with the right strategies and collaborations. Organizations that prioritize education, proactive measures, and cooperation likely find themselves on the winning side of this ongoing battle.




