Table of Contents
Dental implants have revolutionized restorative dentistry by offering a durable and natural-looking solution for missing teeth. The success of these implants relies heavily on the materials used, which must be biocompatible, strong, and capable of integrating seamlessly with the jawbone. Understanding these materials helps patients appreciate the science behind their long-term functionality and reliability.
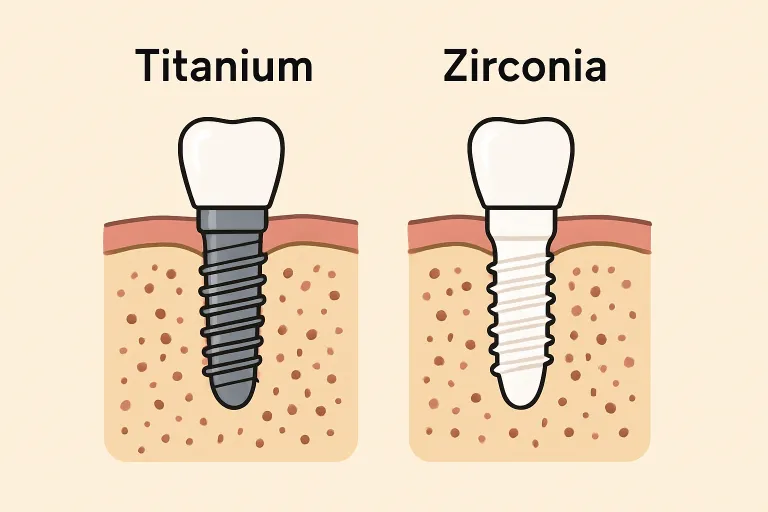
Most dental implants today are made from titanium or zirconia, both of which are known for their exceptional strength and biocompatibility. Titanium has been widely used for decades due to its ability to fuse with bone, a process known as osseointegration. Meanwhile, zirconia offers a metal-free alternative that appeals to patients seeking more aesthetically pleasing options. For those considering dental implants Tulsa OK, learning about these materials can help in making informed choices about treatment options and outcomes.
Ongoing research continues to improve implant materials, enhancing their resistance to wear, corrosion, and bacterial buildup. These innovations ensure better comfort, aesthetics, and longevity, setting new standards for dental restoration.
Titanium: The Gold Standard
Most dental implants are crafted from titanium due to its strength, lightweight nature, and compatibility with the human body. Titanium readily bonds with bone via osseointegration, providing stability and feeling like a natural part of the jaw. Commercially pure titanium, particularly Grade 4, is frequently used due to its strength and flexibility, which enable it to withstand chewing forces and enhance durability. Additionally, it is hypoallergenic and has a proven history of success, often lasting for decades or even a lifetime with proper care.
Zirconia: An Alternative Ceramic
As awareness of metal allergies increases, zirconia has gained popularity as a metal-free alternative. This biocompatible, tooth-colored ceramic provides a natural appearance, especially for visible front teeth. Patients who are sensitive to metals or wish to avoid them often select zirconia for added peace of mind. It also resists plaque buildup and corrosion, which benefits gum health. However, zirconia is more rigid and brittle compared to titanium.
Emerging Materials in Dental Implants
Thanks to advancements in biomaterials, researchers are investigating innovative options such as bioactive glass-titanium composites. These materials leverage titanium’s strength along with bioactive properties that encourage cellular growth, leading to faster bone bonding. Research also examines polymers and hybrid materials that provide greater flexibility and reduce stress at the implant site. While some of these are not yet publicly available, ongoing developments hold the promise of more reliable, tailored solutions for patients with diverse needs.
Coatings and Surface Treatments
Success in dental implant procedures largely depends on surface features that facilitate bone integration. Improved treatments, such as hydroxyapatite, titanium oxide, and calcium phosphate coatings, help accelerate healing by resembling natural bone minerals. Texturing and micro-etching increase the contact area, enhancing stability and cutting down recovery time. Current research explores new coatings and nano-treatments to boost the safety, efficiency, and lifespan of implants.
Customized Implants for Individual Needs
Recent developments in digital imaging and manufacturing have enabled the creation of root-analogue dental implants (RAIs), made from titanium or zirconia to replicate a patient’s natural tooth root. Using 3D scanning, digital planning, and additive manufacturing, dentists can produce highly accurate implants that can be placed immediately after extraction. This approach reduces invasiveness, lessens the need for bone grafts, and provides advantages such as quicker healing and greater comfort, especially in complex cases involving bone loss or challenging jaw regions.
Considerations for Choosing Implant Materials
The material selection process should always be a collaborative effort between the patient and the dental professional. Key factors influencing the decision include:
- Biocompatibility: The material must integrate with bone and tissue without causing adverse reactions, such as allergies or inflammation. Some patients may require allergy screening or additional tests.
- Mechanical Strength and Durability: Materials should withstand decades of chewing, with back teeth requiring more resistance due to the higher pressure they experience.
- Aesthetic Requirements: For visible teeth, materials that mimic natural tooth color are preferred for a seamless look. The gum line and skin tone also influence the best choice.
- Budget: Material costs vary. Titanium implants are typically the most affordable option, while ceramic and composite options may be more expensive but offer additional benefits.
Additional considerations include how quickly you need the restoration, any health issues or medications you may have, and lifestyle factors such as smoking, which can affect healing. Discussing these topics with your provider is essential for a tailored, successful result.
Final Thoughts
Understanding your dental implant options enhances confidence and control. Although titanium remains the most popular material, zirconia and composite options provide additional customization choices. The best material depends on your health, lifestyle, budget, and personal goals. Consulting a dental professional can help you determine the most suitable option for your needs. Being knowledgeable empowers you to confidently achieve a durable, restored smile.